The future of software UX: an early glimpse into AI’s impact
How Artificial Intelligence might shape the next generation of software UX

As I contemplate the recent advancements in natural language AI, particularly GPT, I feel both excited and a little nervous about what the future holds for software and humanity. Like many of us, I’ve been pondering how AI will impact and reshape our software user experiences. While it’s possible that AI might replace jobs in the future, I choose to view this as an opportunity to learn and adapt. Based on my early observations and reflections, I’d like to share some thoughts on how software UX might evolve with AI, specifically in the area of natural language processing. Although these insights may apply to consumer products, my focus here is on B2B SaaS products.
AI augments the existing experience
It’s still early days when it comes to integrating AI directly into products, but we’re all witnessing exponential growth in its capabilities. Many companies have already attempted to incorporate AI capabilities into their applications. AI advancement offers a vast opportunity to get to know your users, the tasks they care about, and their behavior.
While a universal conversational UI may still be out of reach, AI is already making significant strides in enhancing existing user experiences. By analyzing user behavior and preferences, AI can generate personalized recommendations, streamline complex workflows, and help users navigate software more efficiently. As designers, our goal is to seamlessly integrate AI into software, creating intuitive interfaces that allow users to fully utilize these intelligent systems.
Content creation
AI has become a valuable tool for content creators. By using AI’s ability to analyze data and generate human-like text, writers and marketers can save time and produce high-quality drafts. With AI, content creators can focus on refining the narrative and improving readability, while still exploring new topics and approaches. GPT, for instance, can help extract relevant information and generate creative ideas or headlines. It’s no wonder why AI has become one of the most popular tools for content creation.
AI advancements have also impacted music and artwork creation. Although models like OpenAI DALL·E, Stable Diffusion, Midjourney, and Adobe Sensei GenAI cannot yet entirely replace the conventional creation process, they have enabled designers and non-designers alike to create inspiring works of art with unprecedented quality and speed.
Query/script generation
AI is making coding more efficient and less prone to errors. Tools like GitHub’s Copilot are already demonstrating how AI can assist developers with code generation. GPT analyzes existing code repositories and provides context-aware suggestions, helping developers streamline the coding process while reducing errors. By understanding the intent behind the code, GPT can also generate relevant documentation and comments, making the codebase more accessible and maintainable. Additionally, GPT can offer insights into coding best practices and potential optimizations, fostering an environment of continuous improvement and learning for software developers.
Moreover, products like HEX Magic have extended the reach of GPT further to data scientists and analysts alike, making writing queries a breeze using natural language.

Tools like CoPilot and HEX Magic are making it easier for engineers and data scientists to switch between programming languages, regardless of their level of expertise. With these tools, the learning curve for a new programming language or SQL is much less steep. Engineers can now write queries using natural language, which blurs the line between different job functions.
However, we should keep in mind that the technology still hasn’t matured and could lead to erroneous and cost-prohibitive queries, as a recent study by Single Origin suggested:
When it comes to SQL analysis, cost and accuracy requirements make the current publicly available GPT-4 model not suitable for production environments. LLMs have a way to go yet in the SQL domain.
AI will disrupt established patterns
With the introduction of new and enhanced experiences, and as AI continues to evolve, traditional design patterns are being disrupted, and some may become obsolete. More advanced and context-aware AI-driven solutions will replace some of these patterns, and we are barely scratching the surface of what is possible. Designers will need to stay agile and adapt to these changes, rethinking established design principles and embracing new approaches that cater to the evolving needs of users in this AI-driven era.
Data entry
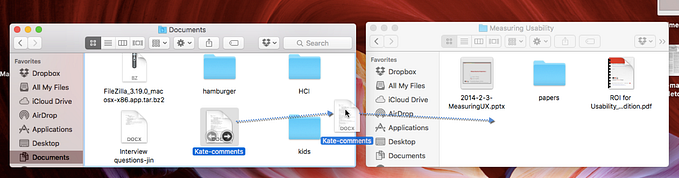
A significant portion of enterprise SaaS workflows involves cleaning and updating spreadsheets, as well as moving them from one system to another. These tasks can be some of the most tedious and frustrating workflows in any SaaS. One example of complex manual or semi-automated data mapping processes is Tableau’s data mapping tool.
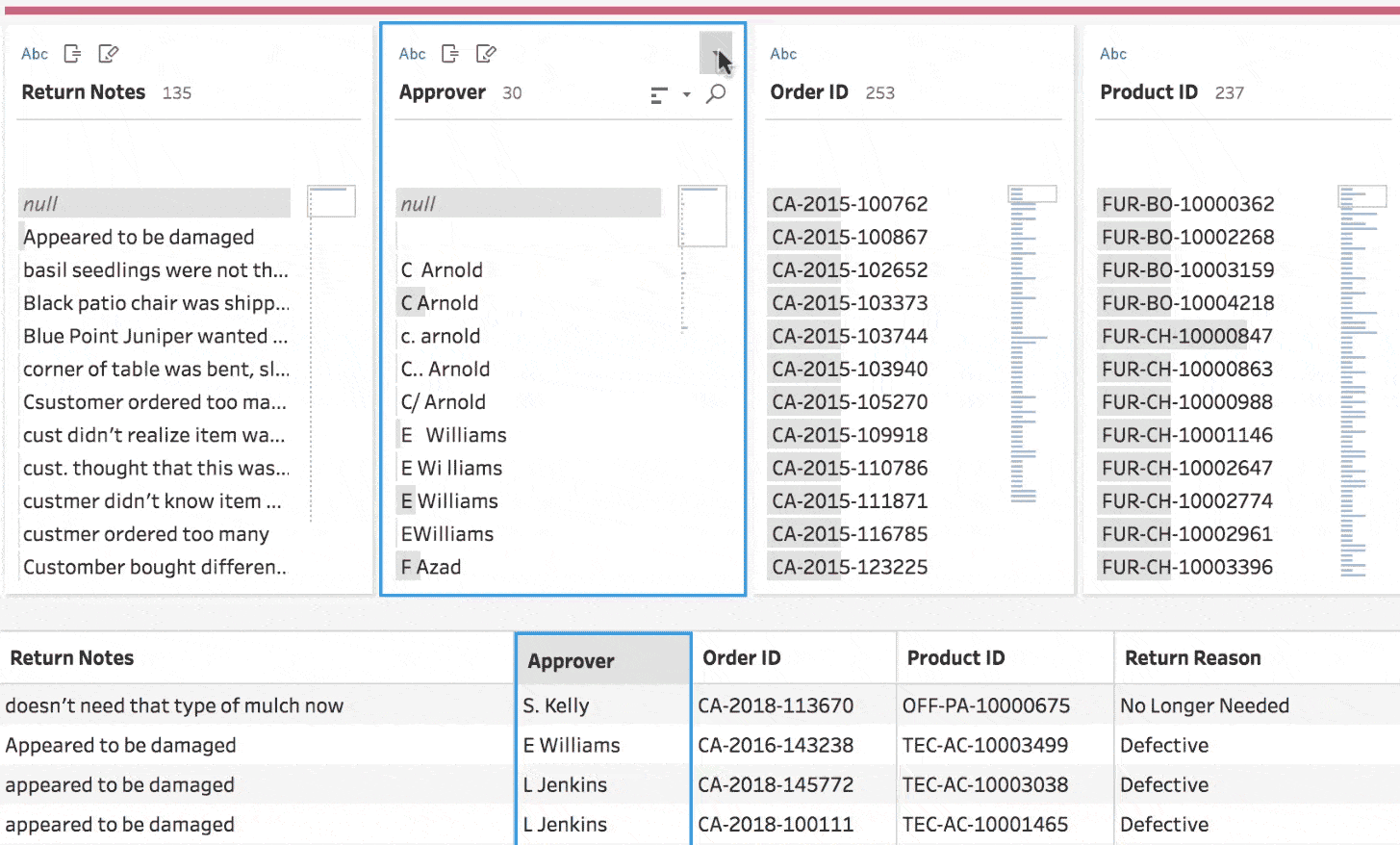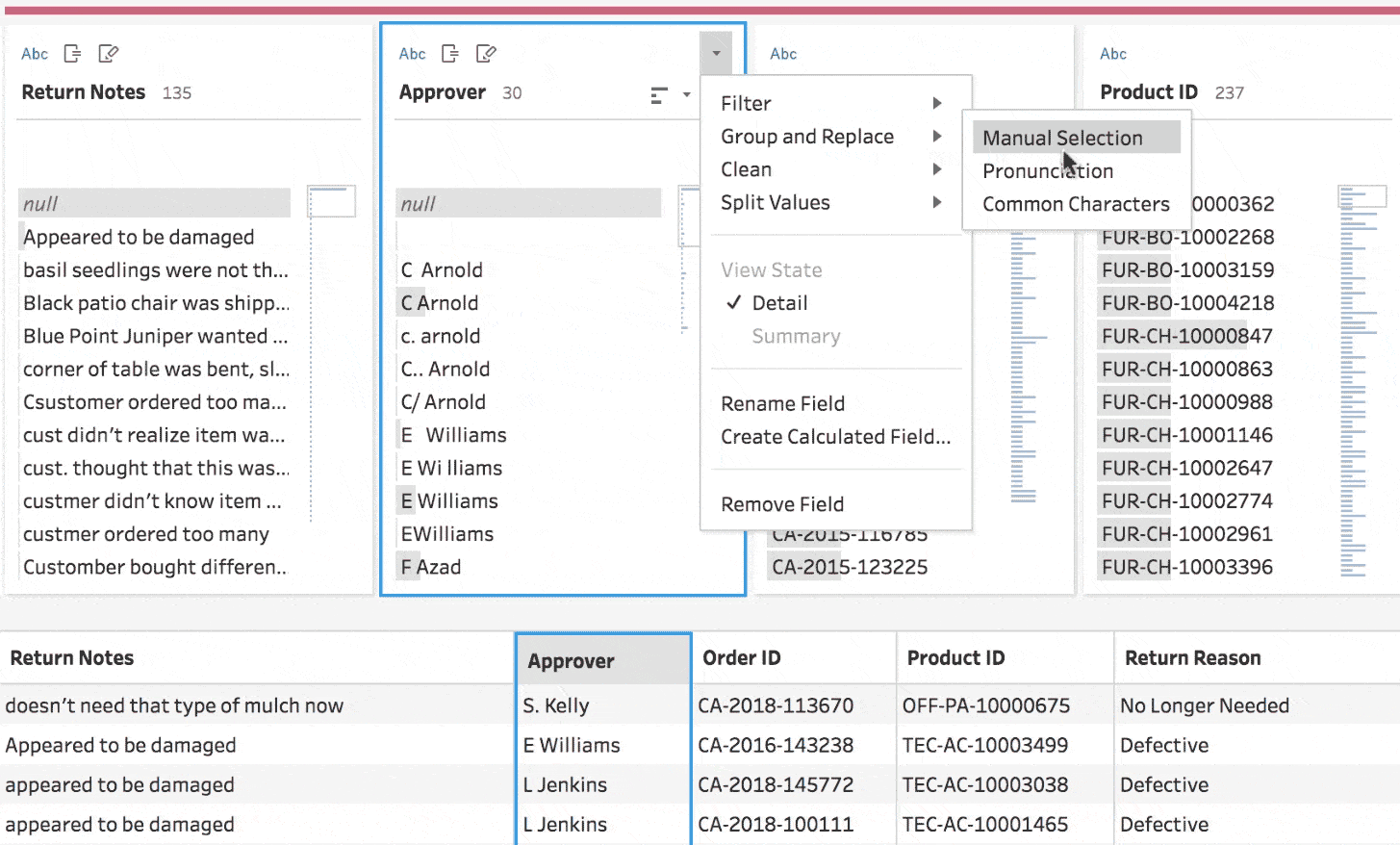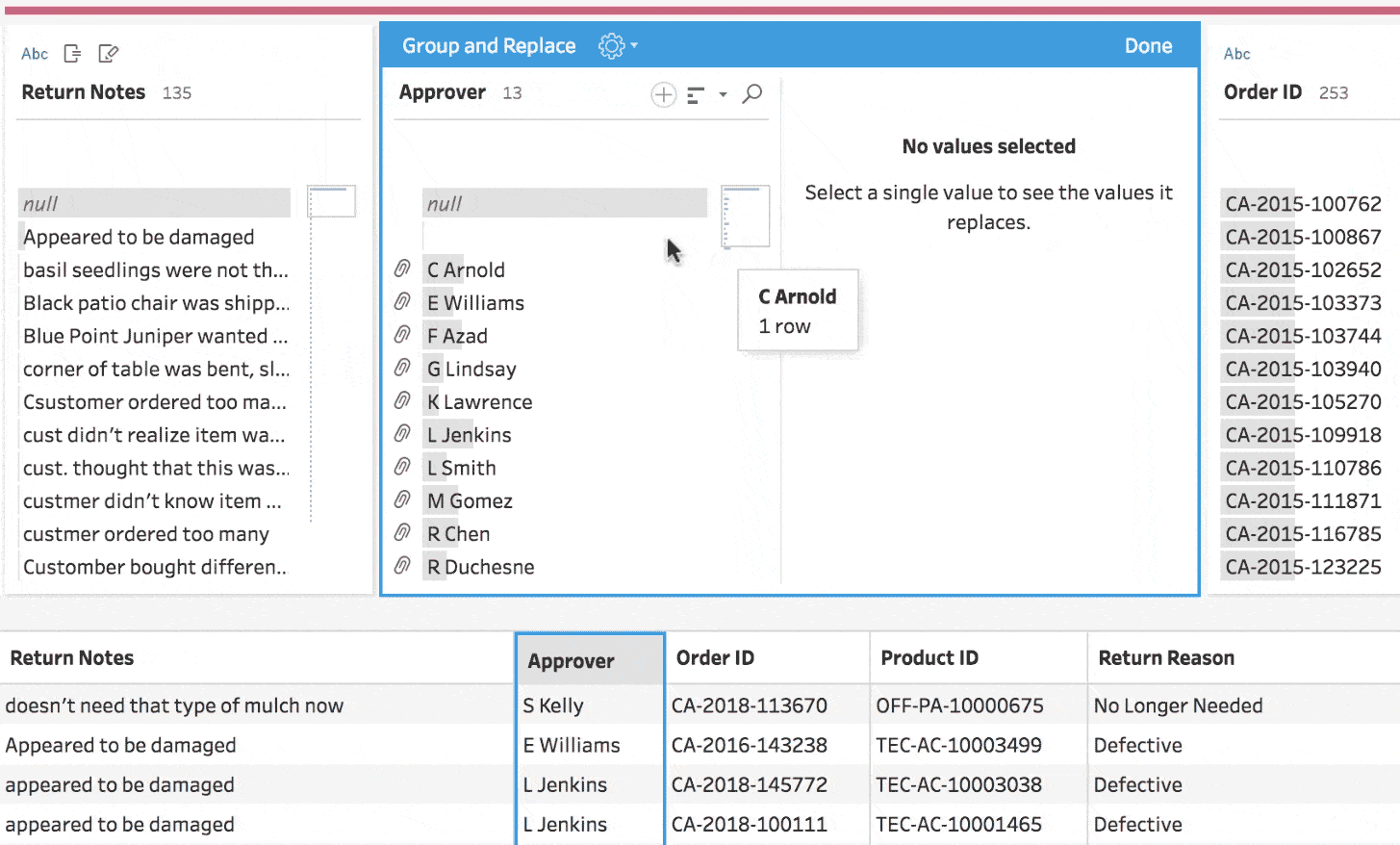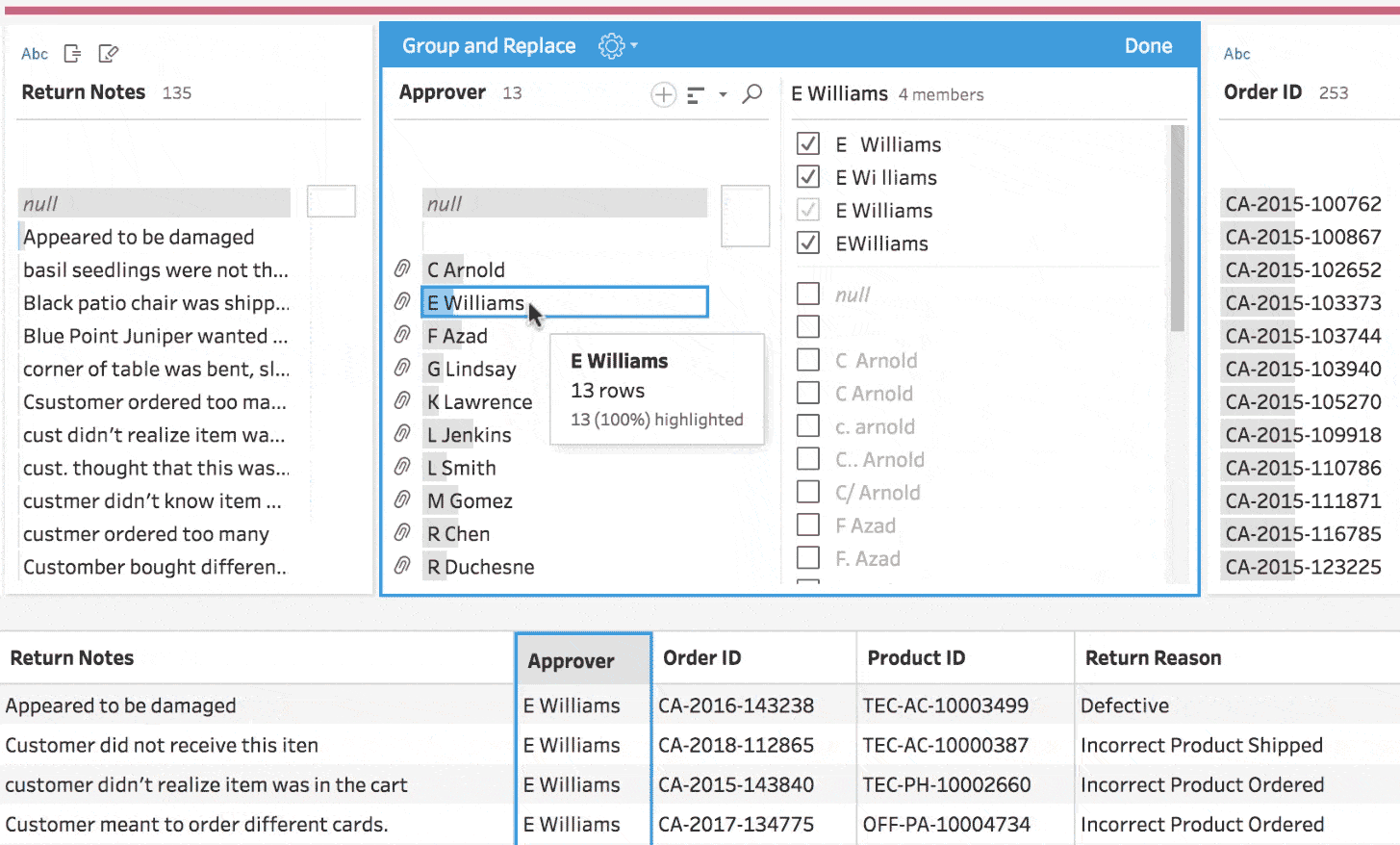
High-quality automated data mapping was implemented using complex algorithms in the past and is limited to advanced data tools, and now could be made possible for every software.
Despite not being initially designed for comprehensive data preparation, AI technologies like large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated their capacity to handle a significant portion of these tasks effectively. As we move towards artificial general intelligence (AGI), manual data mapping between systems will likely be replaced by AI-driven solutions.
By tackling tasks such as data mapping, identifying missing fields, and fixing typos, AI is reshaping the data entry landscape and delivering remarkable efficiency gains. This evolution enables teams to prioritize high-impact tasks and make more informed decisions, ultimately driving productivity.
As an example, UiPath Clipboard AI enables users to highlight a table in your spreadsheet, then simply point Clipboard AI toward the destination — a form, another app, or another table. Clipboard AI determines where the data should go and pastes it.
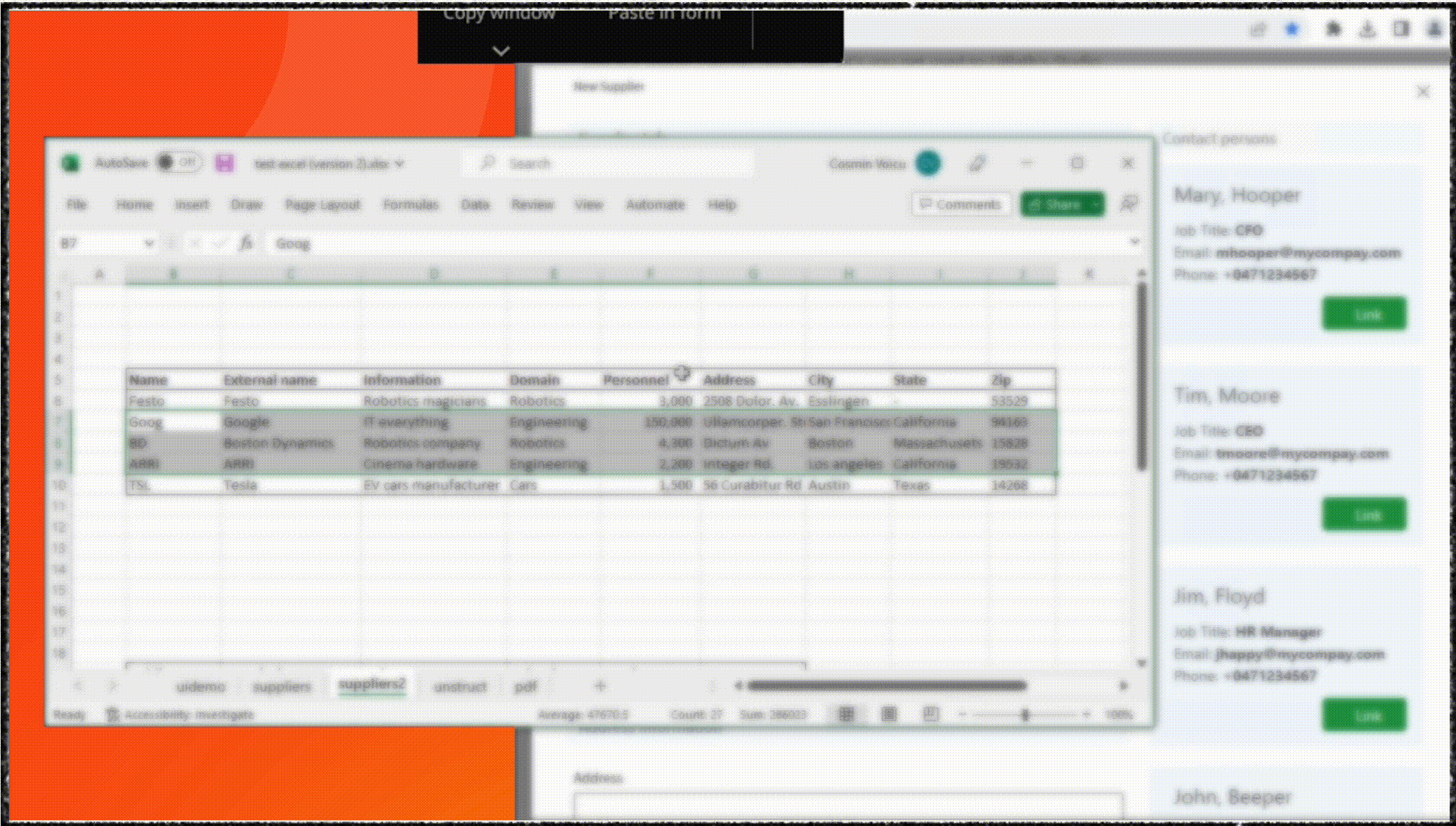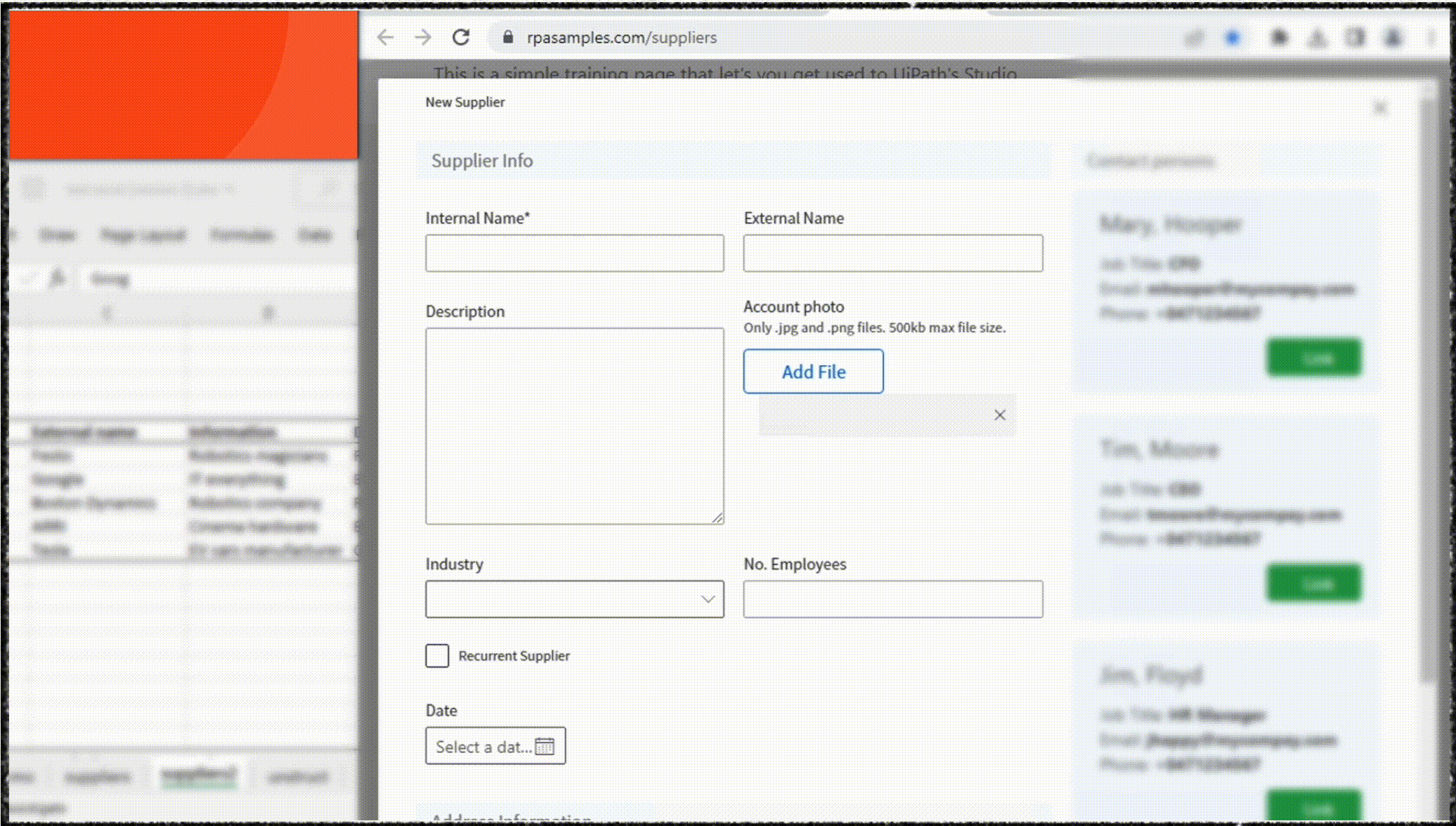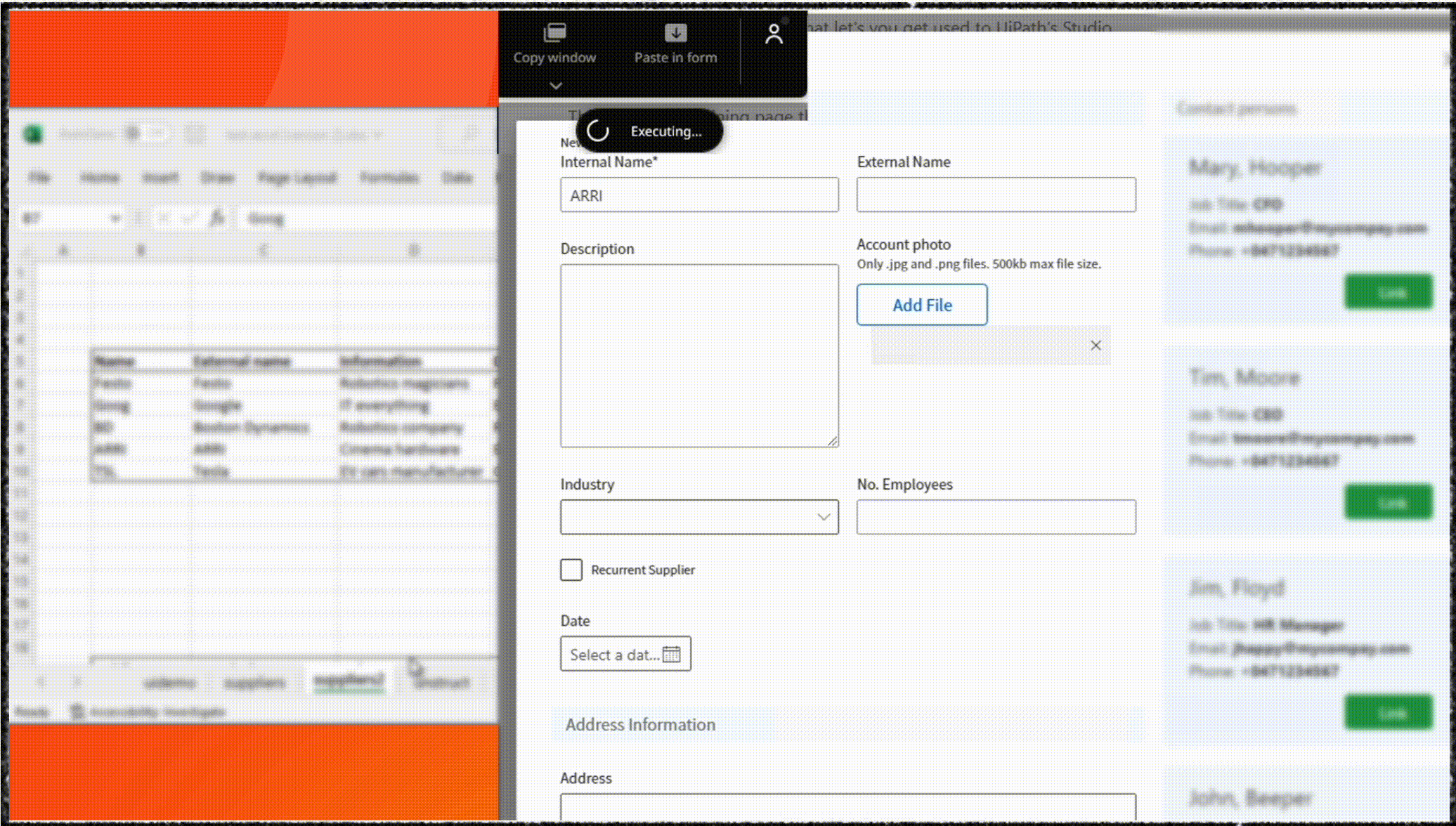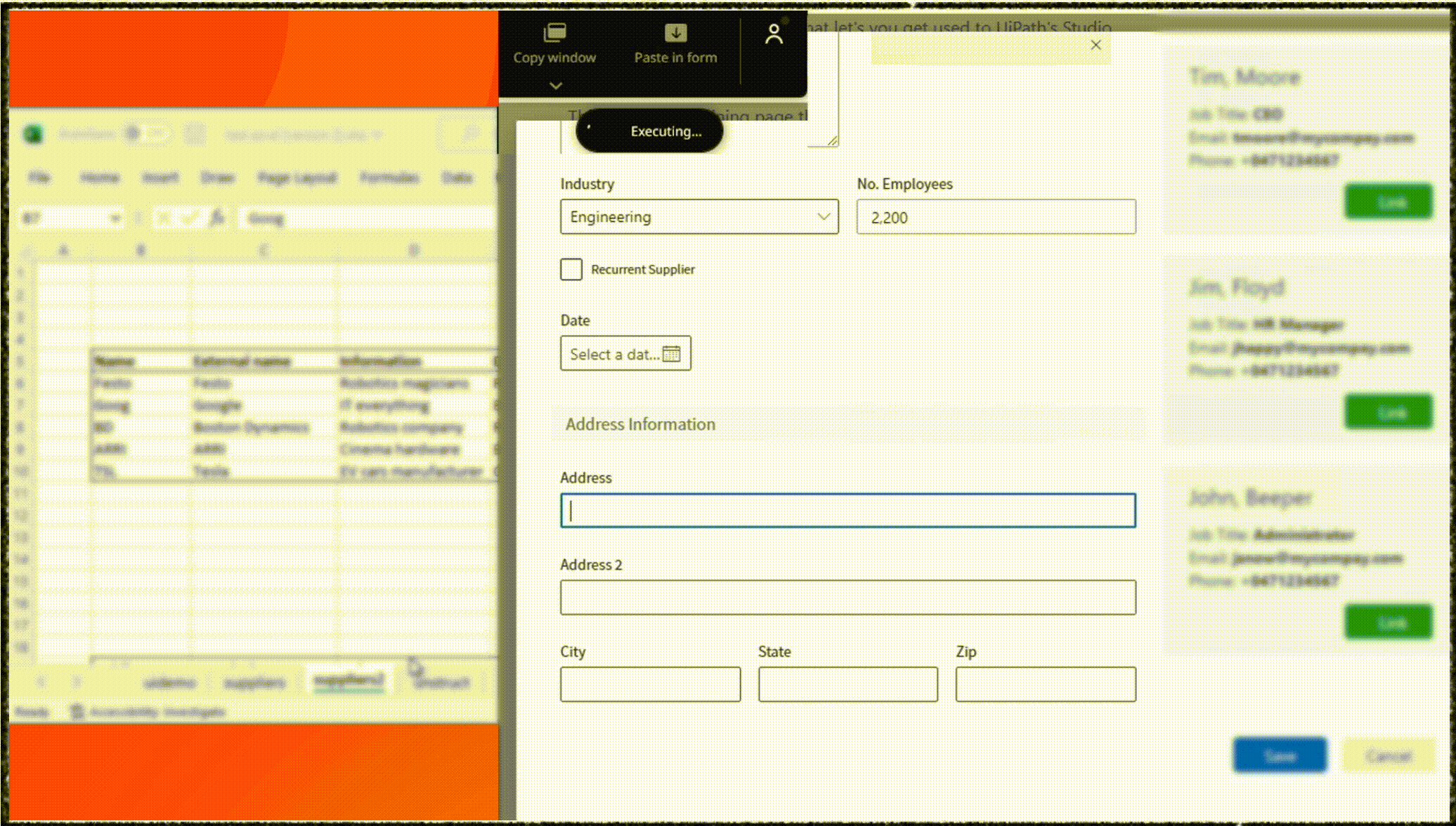
This shift in focus is transforming users from task performers to supervisors who concentrate on reviewing and verifying information, redefining the way software applications approach data entry and enhancing the overall user experience.
Data exploration and analysis
Professionals often struggle with finding and linking the right data to gain insights. Fortunately, AI technologies like GPT have made this task easier. For example, mastering the interactions in Coda was not easy, which limited its perceived value to users, even though it is one of the most powerful document applications. However, by integrating with GPT, Coda AI now allows you to link multiple software and create an aggregate data view using natural language. This has made the whole process more approachable and user-friendly, allowing professionals to work more effectively and efficiently.
Salesforce has also introduced a new feature called Einstein GPT, which serves as a personal assistant for Salesforce app users. With just a simple request for data, the assistant can deliver insights in real time. The possibility of having a central control panel that connects to all your applications, not just Salesforce, is exciting.

In fact, products like HubSpot’s ChatSpot have already made it effortless for users to perform tasks like adding a new contact through the conversational interface. It’s amazing to see how AI technologies like GPT are simplifying our day-to-day tasks, making our work lives more efficient and productive.

While it’s true that some may argue that AI technologies like GPT-4 aren’t the best fit for browsing, as content switching can be cumbersome, I can envision a future where every connected app is linked to a central dashboard. Users would get an embedded snippet for every question or task they perform and would only need to click through the links when they need to browse and explore. This would work similarly to Google, but the difference is that you can ask questions and perform tasks.

Data and information validation
Handling invalid, incomplete data or grappling with error-ridden materials presents a significant challenge for both users and software developers. These issues frequently give rise to complications such as imprecise tax withholdings in HR/payroll software, suboptimal marketing expenditures aimed at inappropriate customer segments, and legal agreements that unjustly disadvantage one party.
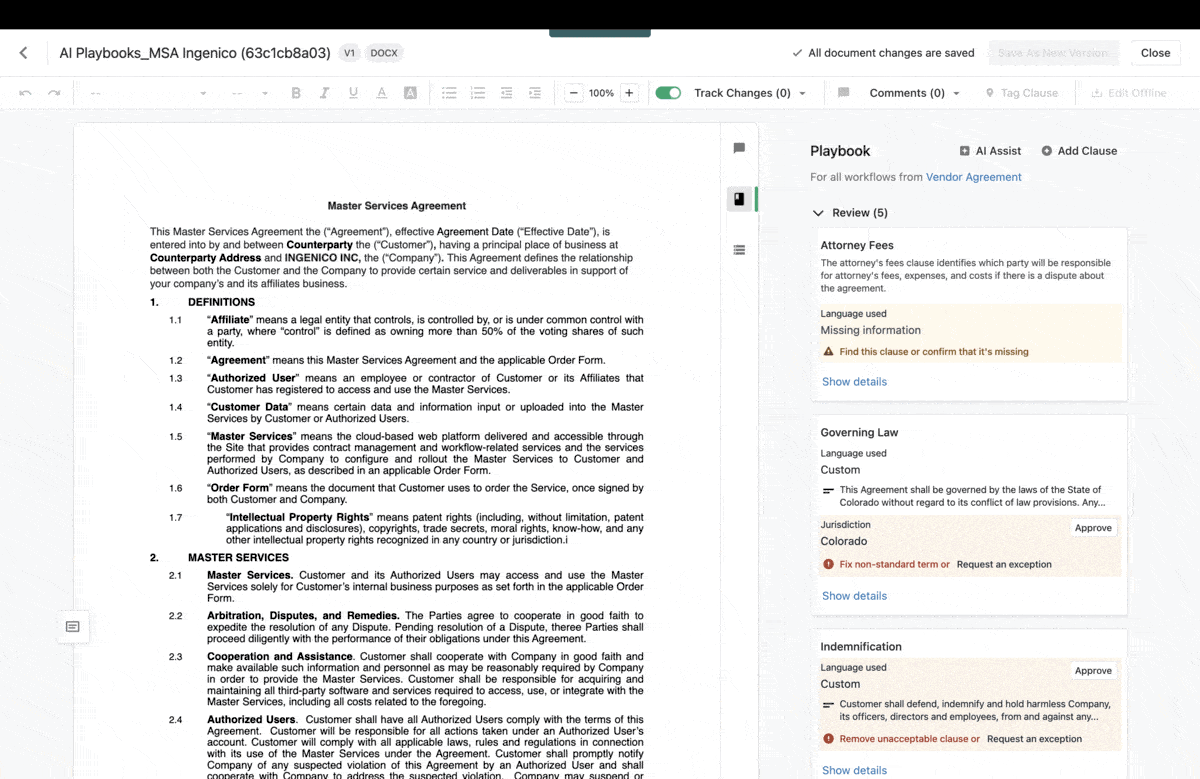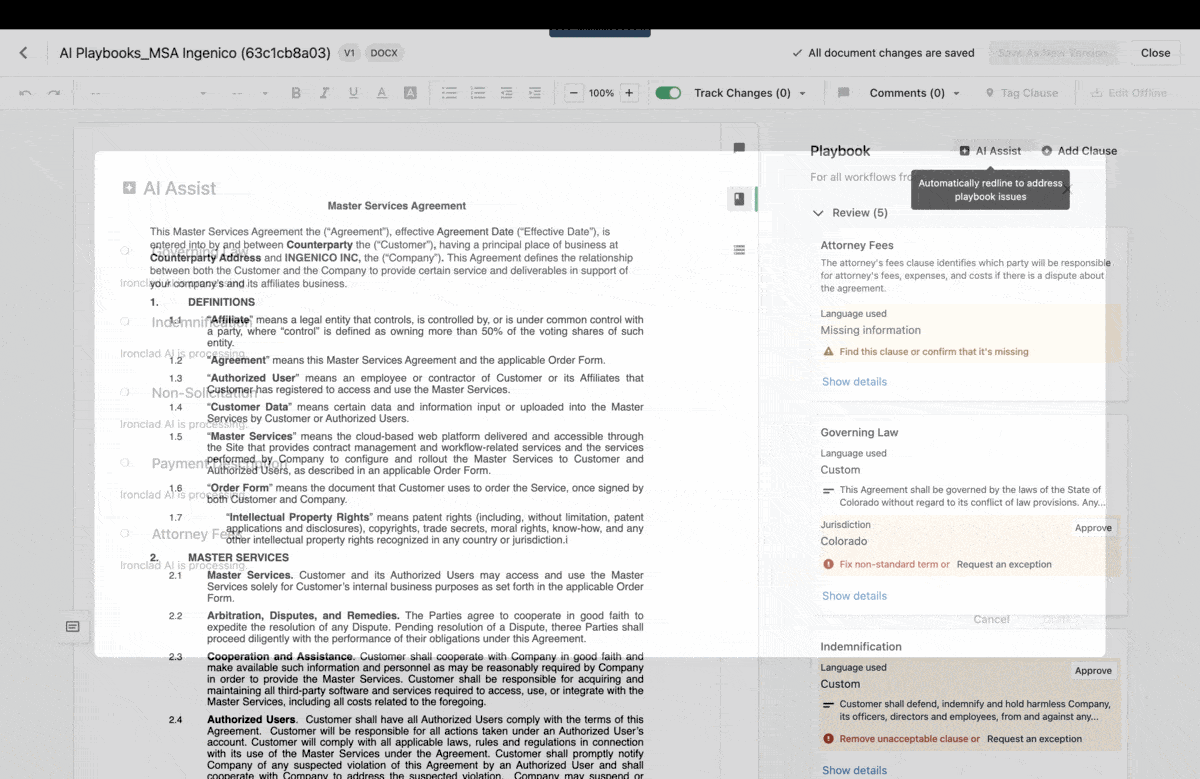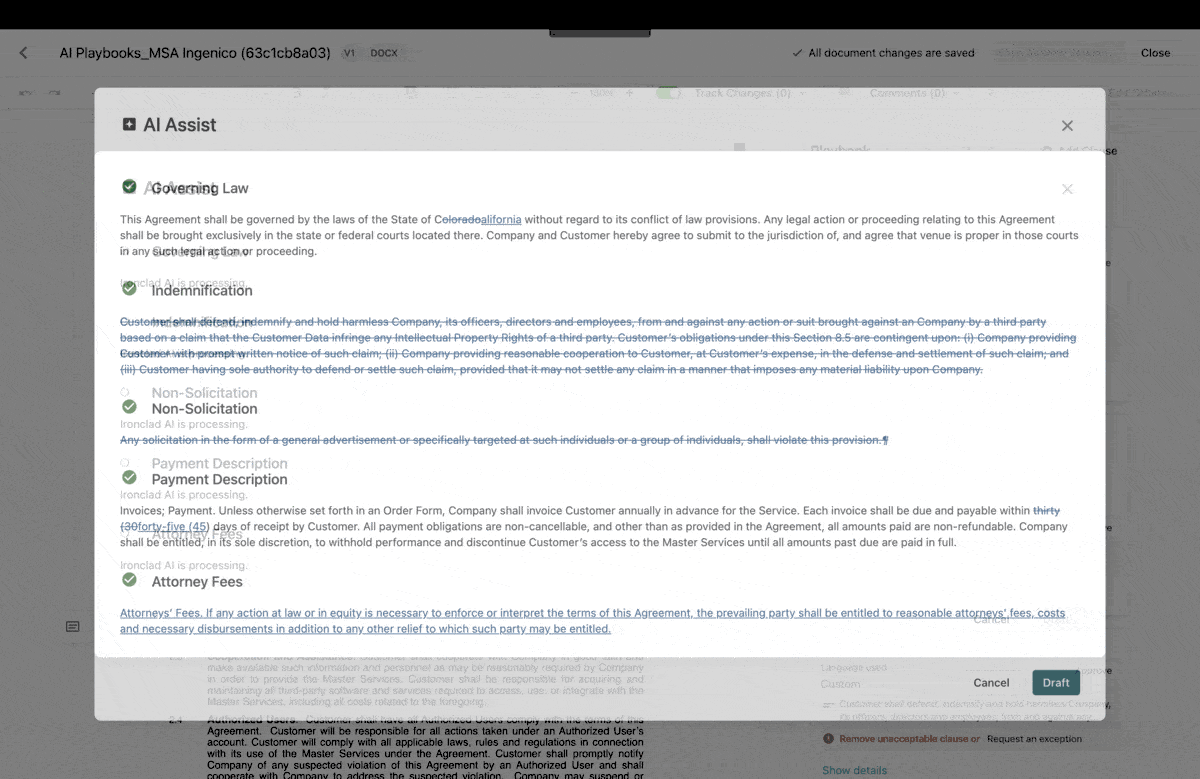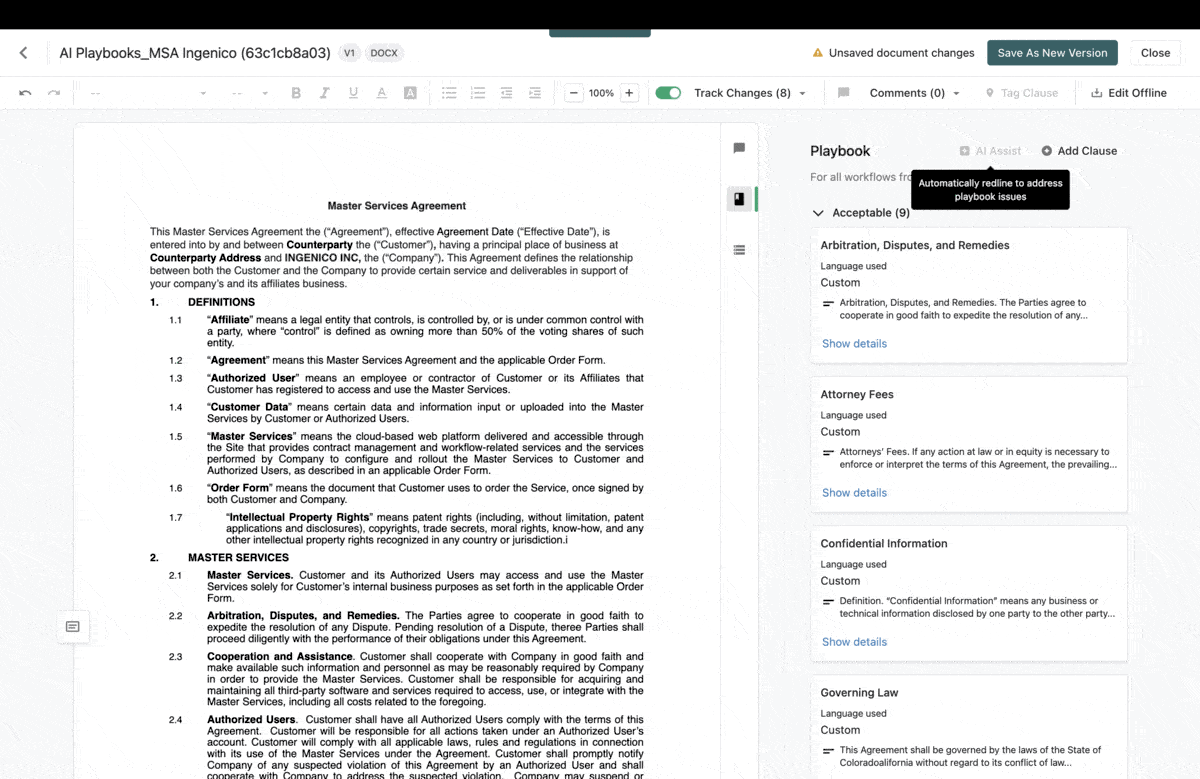
By utilizing the capabilities of artificial intelligence, users can receive timely notifications or suggestions to address any data discrepancies. For example, Ironclad AI simplifies the contract review process by highlighting the most important elements for users to examine and identifying any clauses that require human attention. This approach strikes an ideal balance between automation and user oversight, creating a more efficient and reliable experience for everyone involved.
Chatbot
Although chatbots are here to stay, it is likely that the setup and workings of the technology will be simplified in the future. Companies such as Intercom are already embracing this new AI bot world and have introduced AI bots to their platform. Previously, creating a script in Intercom was a cumbersome process for setting up chatbots, and all the scripts needed to be actively maintained. However, with the introduction of AI bots, this process will likely become a thing of the past.

Search
One area that has been heavily disrupted is navigation in software and documentation sites. Due to the complexity of such systems, users often struggle to find information or capabilities and perform tasks efficiently. Search solutions like Algolia aim to address these pain points. However, extensive customization is typically necessary to achieve optimal flexibility and performance. The integration of new AI models, such as GPT, has significantly shortened the path to value. As Algolia’s CTO, Sean Mullaney, has said:
LLMs are fundamentally changing the way search algorithms work. Traditional search engines match individual words from a query with the words in a large index of content, but LLMs effectively understand the meaning of words, and can retrieve more relevant content.

Professional tool
Companies such as Adobe and Autodesk have developed complex and powerful tools that enable designers to achieve anything and have precise control. While the value of these tools is undeniable, it’s likely that an increasing number of non-designer users will begin to adopt AI-generated content. Even professional designers will increasingly use AI-enabled versions to explore visual directions and expedite processes.
Personalization
AI can generate personalized recommendations and streamline complex workflows, enabling designers to create more intuitive and efficient user experiences. AI-powered systems can adapt to user behavior and preferences, necessitating designers to re-evaluate traditional design patterns, such as dashboards, and develop context-aware solutions. As detailed by Nicole Gallardo:
AI algorithms learn from user behavior and preferences, allowing for more personalized and tailored design solutions. Designers can do things like create more accurate and nuanced user profiles that are based on real data and insights, which in turn helps them create more targeted and effective designs.
Embracing the challenges of AI-Powered UX
As AI-powered products become more widespread and reach users with varying levels of technical knowledge, new capabilities bring new challenges. Designers need to reconsider guiding principles to ensure that these products are reliable and valuable to users.
Reliability: AI-powered features should provide accurate and dependable information to users, particularly in fields such as healthcare and education where misinformation can have serious consequences. Designers should aim to ensure that AI systems are well-trained and tested, and consider incorporating verification processes to maintain a high level of accuracy.
In some cases, AI systems may also require human oversight. An AI companion may be safe for doctors to use, but not for patients. Google’s People+AI Guidebook provides some useful guidance on designing AI systems that are both effective and ethical:
When determining how much to automate your product flows, think about the stakes of your product, and the level of comfort that users may have with your type of product.
In low-risk, well-established products, like content recommendation systems, you might choose to prioritize a more heavily automated product flow where user control is available but optional.
However, when onboarding to a new type of product, or in high-stakes situations, errors can be particularly problematic, and can corrode user trust and potentially cause dangerous situations. In such cases, design your system to give users more control over the system.
It’s important to recognize that even for non-critical tasks, using AI inappropriately could have negative impacts. For example, while auto-generating SQL queries might seem convenient, it’s vital to keep in mind that this could potentially result in less optimized queries, which in turn could lead to negative user perceptions about the product. Therefore, it’s crucial to carefully consider the trade-offs and make informed decisions to ensure the best possible outcomes.
Transparency: Being forthright about the capabilities and limitations of AI is crucial. Since AI can be complex and challenging to comprehend, it is vital to inform users about any uncertainties or unknowns related to its operation. This approach can help manage users’ expectations and enhance their experience. For instance, Notion AI has a disclaimer that states, “AI responses can be inaccurate or misleading.”

Trust and Privacy: To ensure that users feel comfortable with the AI-powered system, it’s essential that they understand how their data is being used, stored, and protected. As AI becomes more mainstream, enterprises are increasingly concerned with safety and compliance, and they will likely demand greater clarity in privacy policies and vendor agreements. To address these concerns, we must communicate clearly about obtaining user consent, anonymizing data, and setting data retention policies.

User control: It’s important to empower users by giving them control over AI-powered features. This includes options to adjust settings, provide feedback on AI-generated suggestions, or choose between manual and AI-assisted options. By prioritizing user needs and providing them with customizable experiences, designers can create more user-centric and empowering products. As Google’s People+AI Guidebook advised:
Allow your users to supervise automation and take back control when needed, rather than automating across the board.
This is helpful to users in a number of ways, including:
Building comfort in new or high-stakes situations with the support of controls to override the system if needed.
Giving them a way to complete their task when the system doesn’t work as intended.
Adobe Firefly is an excellent example of a design tool that incorporates the latest AI capabilities while still retaining a high level of vector control. This empowers professional designers to achieve the perfect balance between artistry and precision, resulting in the outstanding final artwork.

Midjourney’s content curation method primarily relies on trial and error, which makes it a useful tool for exploring the visual direction and brainstorming. However, it may not be as effective for refining work due to its lack of pinpoint accuracy. Nonetheless, this approach can still provide valuable insights and inspiration, especially when combined with other methods of content curation.
Reversibility: Users should feel empowered when using AI-driven applications, with the ability to undo changes or return to previous states if needed. Designers must thoughtfully implement safeguards and clear mechanisms for users to backtrack and correct AI-generated results. This ensures that users maintain control over their data and workflows. A great example of a product that does this well is OpenAI’s ChatGPT client, which keeps all historical versions to make it easier to compare. By focusing on user needs and preferences, designers can create more inclusive and adaptable AI-powered products that are accessible to users with diverse abilities and needs.

Accessibility: In order to make AI-powered products more user-friendly for everyone, it’s important for designers to consider the needs of users with diverse abilities and preferences. By incorporating inclusive design principles and keeping accessibility requirements in mind throughout the design process, designers can create more adaptable and welcoming experiences.
Different users might have different preferences when it comes to interacting with a product. Some might prefer traditional visual interfaces, while others might prefer conversational interactions. To create products that are truly inclusive, designers must strike a balance between these different preferences.
Crossing the chasm
Adjusting to the new norm won’t be easy for users and designers alike. During this paradigm shift, it’s crucial for designers to guide users through the transition, making sure they feel comfortable and confident with the changes that AI brings to their digital experiences. By being mindful of the learning curve and providing appropriate support, the shift can be made easier for users while maintaining their trust and fostering positive relationships between users and the AI-powered tools they interact with.
The rise of AI and conversational UI presents both challenges and opportunities for designers in the enterprise space. It is acknowledged that squeezing the entire software stack into a central dashboard that allows users to interact with all connected apps is still a far-fetched dream for the foreseeable future. Despite that, the journey to that future promises to be an interesting one. By staying open-minded and adaptable, designers can navigate these changes and continue to create meaningful and engaging user experiences in the age of AI.